Lesson 1 - Part A
| Arabic | |
|---|---|
| Arabic: al-ʻarabiyyah/ʻarabī | |

al-ʿArabiyyah in written Arabic (Naskh script)
| |
| Pronunciation | /al ʕarabijja/, /ʕarabi/ |
| Native to | Countries of the Arab League, minorities in neighboring countries: Israel, Eritrea, Mali, Niger, Kenya, Chad, Senegal, South Sudan, Ethiopia, Iran, Turkey, Madagascar, Tanzania, Mozambique etc. |
Native speakers
| 290 million (2010)[1] |
Language family
|
Afro-Asiatic
|
Standard forms
|
Modern Standard Arabic
|
| Dialects |
Western (Maghrebi)
Central (incl. Egyptian, Sudanese)
Northern (incl. Levantine, Mesopotamian)
Peninsular (Gulf, Hejazi, Najdi, Yemeni)
|
Writing system
| Arabic alphabet Arabic Braille Syriac alphabet (Garshuni) Hebrew alphabet (Judeo-Arabic languages) Greek alphabet (Cypriot Maronite Arabic) Latin script (Maltese) |
Signed forms
| Signed Arabic (national forms) |
| Official status | |
Official language in
| Modern Standard Arabic is an official language of 27 states, the third most after English and French[2] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | ar |
| ISO 639-2 | ara |
| ISO 639-3 | ara |
| Glottolog | arab1395[3] |
| Linguasphere | 12-AAC |

Countries where Arabic holds official status
| |
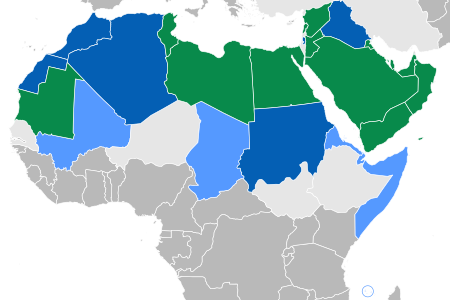
Use of Arabic as the sole official language (green) and an official language (majority: dark blue; minority: light blue)
| |




